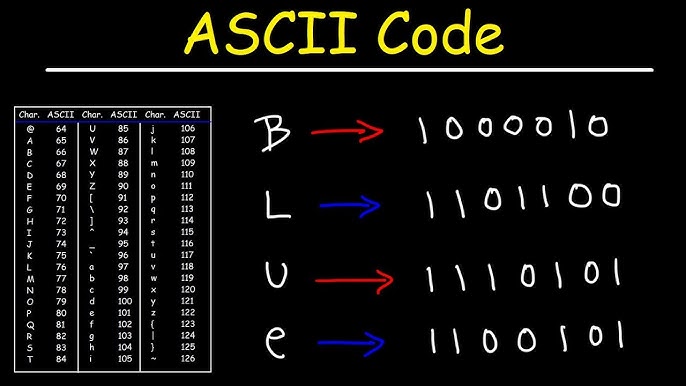
Welcome to Techgues. Converting binary to ASCII is a fundamental skill in computer science that transforms strings of 0s and 1s into human-readable text. This process may seem daunting at first, but with a clear understanding of the steps involved, it becomes straightforward and approachable. Whether you are a beginner exploring the basics of data encoding or a seasoned coder seeking a quick refresher, this guide will walk you through the process with clear explanations and practical examples.
What is Binary and ASCII?
Before diving into the conversion process, let’s clarify the basics:
- Binary: The binary number system is a base-2 system that uses only 0s and 1s to represent data. In computing, all data is ultimately stored and processed in binary, as computers operate using electrical signals that are either on (1) or off (0).
- ASCII: ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) is a character encoding standard that assigns a unique number (from 0 to 127) to common characters, such as letters, digits, and symbols. For example, the letter ‘A’ is represented by the decimal number 65, which is 01000001 in binary.
You Also Read:
What Are Long Status Split videos for Whatsapp?
What Is Hide Last Seen with Mask Chat: Unseen Chat
What Is a Safe Chat App, and How To Use
The goal of binary-to-ASCII conversion is to take a sequence of binary digits, interpret them as ASCII values, and translate those values into readable characters.
Step-by-Step Conversion Process
Converting binary to ASCII is a systematic process. Follow these steps to make it simple:
Step 1: Group the Binary Digits
ASCII characters are typically represented by 8-bit binary numbers (one byte per character). Start by breaking your binary string into groups of 8 bits. For example, if you have the binary string 0100100001100101, divide it into:
- 01001000
- 01100101
Each 8-bit group represents one ASCII character.
Step 2: Convert Binary to Decimal
Next, convert each 8-bit group from binary to its decimal equivalent. You can do this manually by calculating the place values of each bit. Each position in the binary number represents a power of 2, starting from 2^0 (1) on the right to 2^7 (128) on the left.
For example, let’s convert 01001000:
- 0 × 2^7 = 0
- 1 × 2^6 = 64
- 0 × 2^5 = 0
- 0 × 2^4 = 0
- 1 × 2^3 = 8
- 0 × 2^2 = 0
- 0 × 2^1 = 0
- 0 × 2^0 = 0
Add them up: 64 + 8 = 72. So, 01001000 equals 72 in decimal.
Repeat this for 01100101:
- 0 × 2^7 = 0
- 1 × 2^6 = 64
- 1 × 2^5 = 32
- 0 × 2^4 = 0
- 0 × 2^3 = 0
- 1 × 2^2 = 4
- 0 × 2^1 = 0
- 1 × 2^0 = 1
Add them up: 64 + 32 + 4 + 1 = 101. So, 01100101 equals 101 in decimal.
Step 3: Map Decimal to ASCII Characters
Using an ASCII table, find the characters corresponding to the decimal values. For our example:
- Decimal 72 corresponds to the character ‘H’.
- Decimal 101 corresponds to the character ‘e’.
So, the binary string 0100100001100101 translates to the ASCII text “He”.
Step 4: Verify and Combine
Double-check your binary groupings and calculations to ensure accuracy. Combine the characters to form the final text. If the binary string is longer, continue the process for each 8-bit group to build the complete message.
Practical Example
Let’s convert a longer binary string: 01001001001000000110110001101111011101100110010100100000. Break it into 8-bit groups:
- 01001001 (I)
- 00100000 (space)
- 01101100 (l)
- 01101111 (o)
- 01110110 (v)
- 01100101 (e)
- 00100000 (space)
Converting each group to decimal and mapping to ASCII:
- 01001001 = 73 = ‘I’
- 00100000 = 32 = ‘ ‘ (space)
- 01101100 = 108 = ‘l’
- 01101111 = 111 = ‘o’
- 01110110 = 118 = ‘v’
- 01100101 = 101 = ‘e’
- 00100000 = 32 = ‘ ‘ (space)
The result is the ASCII text “I love “.
Tips for Success
- Use an ASCII Table: Keep an ASCII reference handy to quickly map decimal values to characters.
- Check Bit Length: Ensure each group has exactly 8 bits. If the binary string isn’t a multiple of 8, there may be an error in the input.
Automate with Tools: For longer strings, consider using programming languages like Python or online converters to automate the process. For example, in Python, you can use:
binary = “0100100001100101”
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Incorrect Grouping: Splitting the binary string incorrectly can result in incorrect characters. Always count 8 bits per group.
- Leading Zeros: Missing leading zeros in a group (e.g., 1001 instead of 00001001) can cause errors. Pad with zeros if needed.
- Non-ASCII Values: ASCII only covers decimal values 0–127. If a binary group converts to a decimal outside this range, it may not map to a standard ASCII character.
Why Learn Binary to ASCII?
Understanding binary-to-ASCII conversion is valuable for:
- Data Encoding: Learn how computers store and transmit text.
- Debugging: Decode binary data in low-level programming or network protocols.
- Cybersecurity: Analyze encoded messages in challenges like capture-the-flag (CTF) competitions.
You Also Read:
What Are Long Status Split videos for Whatsapp?
What Is Hide Last Seen with Mask Chat: Unseen Chat
What Is a Safe Chat App, and How To Use
Conclusion
Binary-to-ASCII conversion is a simple yet powerful skill that bridges the gap between machine language and human-readable text. By breaking the process into manageable steps—grouping binary digits, converting to decimal, and mapping to ASCII characters—you can decode binary strings with ease. Practice with small examples, use tools to streamline larger tasks, and soon you’ll be converting binary to ASCII like a pro.